-
- Products
- Indoor Household Cords
- Appliance Cords
- General Purpose Short-Length Cords
- General Purpose Extension Cords
- Landscape & Decorating Cords
- Bright Color Extension Cords
- Oil-Resistant Extension Cords
- Cold-Flex Extension Cords
- VividFlex Power Cords
- EXTREME All-Weather Cords
- Cord Management
- Task Lights
- Adapters & GFCI Devices
- Where to Buy
- About
- Careers
- Glossary
- Catalog
- Products
- Indoor Household Cords
- Appliance Cords
- General Purpose Short-Length Cords
- General Purpose Extension Cords
- Landscape & Decorating Cords
- Bright Color Extension Cords
- Oil-Resistant Extension Cords
- Cold-Flex Extension Cords
- VividFlex Power Cords
- EXTREME All-Weather Cords
- Cord Management
- Task Lights
- Adapters & GFCI Devices
- Where to Buy
- About
- Careers
- Glossary
- Blog
-
-

Top Tips for Choosing the Right Power Cord Wire for Your Needs
When it comes to selecting the right power cord wire for your electrical needs, understanding the nuances of various options available in the market is essential. As John Harris, an industry expert with over 15 years of experience in electrical engineering, aptly states, "Choosing the right power cord wire is not just about compatibility; it's about ensuring safety and efficiency for your specific application." With advancements in technology and a plethora of choices, customers often find themselves overwhelmed by the options.
To make an informed decision, it is crucial to consider factors such as wire gauge, insulation type, and the cord’s intended use. Whether you are powering household appliances, industrial machinery, or specialized equipment, the right power cord wire will not only enhance performance but also contribute to the longevity of your devices. In this guide, we will dive deeper into essential tips that will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the most suitable power cord wire, ensuring that your final choice meets both your needs and safety standards.
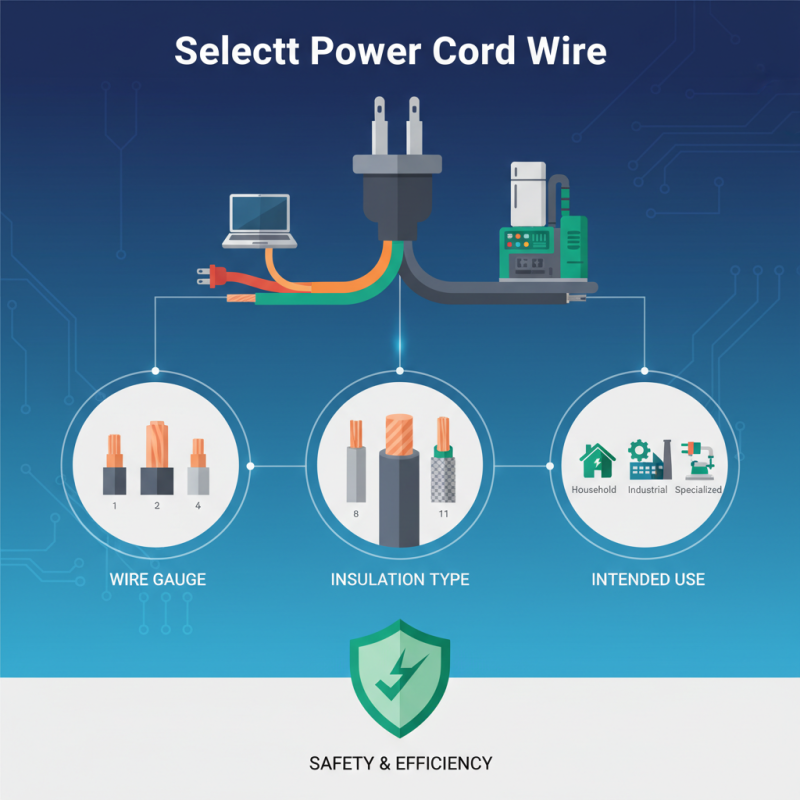
Table of Contents
[Hide]
Understanding the Different Types of Power Cord Wires Available Today
When selecting the appropriate power cord wire for your needs, it's crucial to understand the various types available on the market today. Power cords come in different gauges, lengths, and materials, each designed for specific applications. For instance, according to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), a wire's gauge directly affects its capacity to carry electrical current; a lower gauge indicates a thicker wire capable of handling higher loads. Common household cables, such as those rated for 14 AWG, are generally suitable for devices requiring up to 15 amps, while heavier-duty appliances may necessitate a 10 or 12 AWG wire.
Tip 1: Consider the application of the power cord. If you are powering high-wattage appliances, opt for a thicker gauge to ensure safety and efficiency. For lighter devices, a standard cord may suffice.
Additionally, the insulation material of a power cord plays a significant role in its durability and suitability for different environments. PVC and rubber are common materials; PVC is often used for indoor applications, while rubber can withstand harsher conditions, making it ideal for outdoor use. Research from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) indicates that using the right insulation can enhance the lifespan of your power cords significantly.
Tip 2: Always check the voltage rating and ensure it's compatible with your device's requirements. An undervalued cord may lead to overheating or even electrical fires.
Power Cord Wire Types and Their Applications
Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensuring Safety and Compatibility
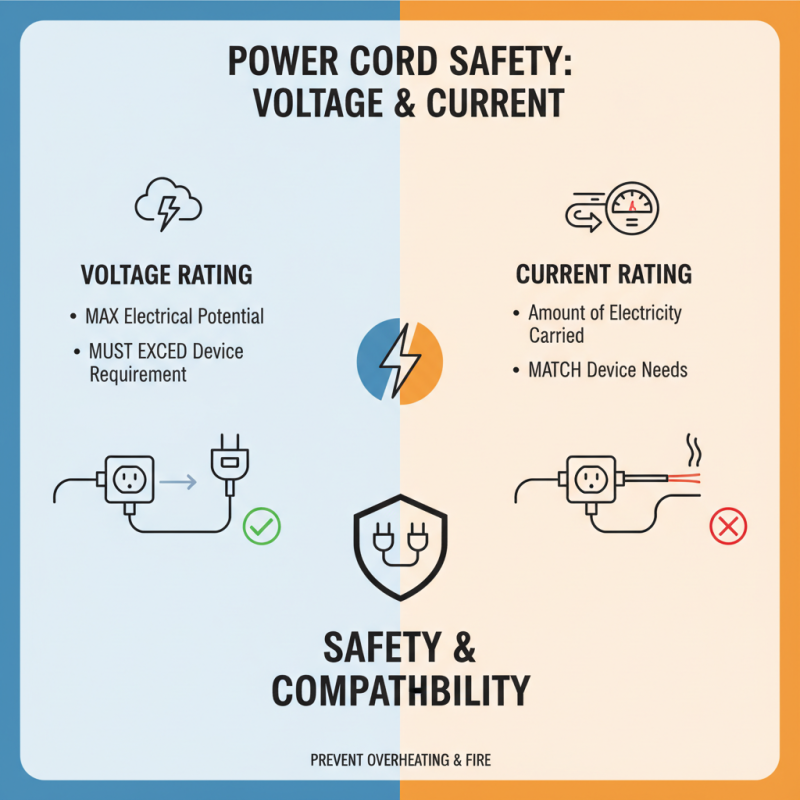
When selecting the appropriate power cord wire for your devices, understanding voltage and current ratings is paramount to ensure both safety and compatibility. Voltage rating indicates the maximum electrical potential that a wire can handle without breakdown, while current rating denotes the amount of electric current the wire can safely carry. Choosing a power cord with voltage ratings that exceed your device requirements is essential to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
Additionally, considering the current rating is vital to prevent damage to your appliances and the power cord itself. Overloading a wire can lead to insulation failure and increased risk of electrical shock. It is crucial to match the current rating of the power cord to the needs of the device—consulting the equipment’s specifications can provide guidance. Ultimately, ensuring that both the voltage and current ratings are appropriate for your specific applications not only enhances performance but also safeguards against electrical hazards.
Material Choices: Copper vs. Aluminum for Optimal Conductivity
When selecting a power cord wire, one of the most critical factors to consider is the material used for its conductors. The two primary options available are copper and aluminum, each exhibiting distinct properties that can influence performance and suitability for different applications. Copper is often regarded as the gold standard in electrical wiring due to its superior conductivity and resistance to corrosion. This makes it an ideal choice for high-performance environments where efficiency and reliability are paramount. Its malleability also allows for easier handling during installation, leading to more secure connections.
On the other hand, aluminum is a lightweight alternative that can be advantageous in specific scenarios, particularly when weight reduction is necessary. While aluminum offers lower conductivity compared to copper, advancements in alloy technology have enabled the production of aluminum wires that can perform adequately for various applications. Additionally, aluminum is generally more cost-effective, making it a budget-friendly option for less demanding tasks. However, when opting for aluminum, it is crucial to ensure the proper gauge and to pay attention to potential expansion and contraction issues that may arise over time. Ultimately, the choice between copper and aluminum should be guided by the specific demands of your project, taking into account factors such as conductivity needs, weight considerations, and budget constraints.
Length and Gauge: Finding the Right Specifications for Your Device
When selecting the appropriate power cord wire for your needs, understanding the specifications of length and gauge is critical. The wire gauge, measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), determines the electrical current a cord can safely carry. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), a lower AWG number indicates a thicker wire, which can handle more current. For example, 14 AWG wires are commonly used for devices requiring up to 15 amps, providing a balance between flexibility and capacity. Conversely, 18 AWG wires are more suited for lower amperage applications, such as small electronic devices, highlighting the importance of matching your wire gauge to your power requirements.
Equally important is the length of the power cord, which can significantly affect voltage drop. The U.S. Department of Energy suggests that for long-distance connections, a thicker wire may be required to compensate for voltage loss. For instance, a power cord of 50 feet with a 16 AWG wire may result in a voltage drop that is noticeable, potentially impacting device performance, especially in appliances and tools that operate on high power. Therefore, taking into account both the length and gauge ensures optimal efficiency and safety for your devices, ultimately prolonging their lifespan and enhancing their operation.
Safety Standards and Certifications to Look for in Power Cords
When selecting the right power cord wire, it’s crucial to prioritize safety standards and certifications to ensure reliable and secure use. One key certification to look for is the Underwriters Laboratories (UL) mark, which indicates that the product has been tested for safety and meets stringent performance standards. This certification not only assures compliance with safety regulations but also helps consumers identify cords that can handle various electrical loads without posing fire hazards or risk of electrical shocks.
Another important certification to consider is the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) endorsement, which guarantees that the power cord adheres to specific safety and performance requirements. Additionally, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) ratings provide guidance on the suitability of cords for different environments and applications. By seeking out products that hold these certifications, users can ensure that their selected power cords are built for durability and functionality, ultimately contributing to a safer working or living space.
Top Tips for Choosing the Right Power Cord Wire for Your Needs - Safety Standards and Certifications to Look for in Power Cords
| Dimension | Description | Safety Standards | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | Indicates the maximum voltage the cord can handle. | UL/CSA Certifications | Suitable for household electronics. |
| Wire Gauge | Refers to the thickness of the wire; lower numbers indicate thicker wires. | AWG Rating | Used for heavy-duty tools and appliances. |
| Insulation Material | Material used to insulate the wire, affecting durability and flexibility. | PVC, rubber | Indoor and outdoor usage. |
| Length | The total length of the power cord. | N/A | Choose based on distance from the power source. |
| Connector Type | Type of connector at the ends of the cord. | NEMA, IEC Standards | Compatibility with devices. |
| Temperature Rating | The maximum temperature that the cord can withstand. | UL 62 Compliance | For high-heat applications. |
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 5 Cable Cords: Essential Choices for Every Tech Enthusiast
-

How to Choose the Right Power Cord Cable for Your Electronics with Expert Tips
-

Enhancing Cable Integrity with Advanced Monitoring Technologies to Prevent Failures
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Power Cord Adapters for Your Devices
-

2025's Top 10 GFCI Power Cords: Safe and Reliable Options for Your Home
-

How to Organize and Manage Electronic Cords for a Clutter Free Space

